competitive advantage
Surfactants Supplier & Distributor
Surface-Active Agents
Introducing Modern Chemical as a Surfactants, aka surface-active agents, supplier and distributor. Modern Chemical supplies high-quality and cost-effective surfactants sourced from around the world to a wide range of industries.
- low-cost, in-spec, and on-time
- commitment to quality
- all-in-one partner
- Unbeatable Price
Surfactant Information
Characteristics of Surfactants
Surfactants, short for surface-active agents, are compounds that lower the surface tension between two liquids or between a liquid and a solid. They are amphiphilic molecules, meaning they have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic components.
What are the 4 Categories of Surfactants?
Surfactants can be synthetic or natural and come in different forms. There are various types of surfactants, or surface-active agents, and they can be broadly classified into four main categories based on their charge:
Anionic Surfactants:
- These surfactants have a negatively charged hydrophilic (water-attracting) head.
- Examples include sodium lauryl sulfate (commonly used in soaps and shampoos), Sodium Dodecylbenzenesulfonate, and soap.
Cationic Surfactants:
- Cationic surfactants have a positively charged hydrophilic head.
- They are often used as fabric softeners and in certain hair conditioners.
- Examples include cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and benzalkonium chloride.
Nonionic Surfactants:
- Nonionic surfactants do not have a charged hydrophilic head.
- They are often used in products where a charged surfactant might interfere with the formulation or performance.
- Common examples include Triton X-100 and polyethylene glycol (PEG).
Amphoteric (Zwitterionic) Surfactants:
- Amphoteric surfactants have both positive and negative charges in the same molecule, making them electrically neutral overall.
- They are versatile and can function as either anionic or cationic depending on the pH of the solution.
- Examples include betaines and amino acid-based surfactants.
Each type of surfactant has specific properties and applications based on its chemical structure and charge, and they are widely used in various industries, including personal care products, detergents, pharmaceuticals, and more.
Industries & Applications of Surfactants
What Industries and Applications Do Surfactants Serve?
Surfactants, also called surface-active agents, are used in a wide range of industries, including personal care, household cleaning, oil and gas, agriculture, personal care, pharmaceuticals, food, paints, mining, biotechnology, environmental remediation, and textiles. They are commonly used in formulations such as soaps, detergents, shampoos, and emulsifiers. In the oil and gas industry, surfactants are used to enhance oil recovery from reservoirs. In agriculture, they are used as adjuvants to increase the effectiveness of pesticides and herbicides. They contribute to product efficiency in areas like cleaning, dispersion, solubilization, and extraction.
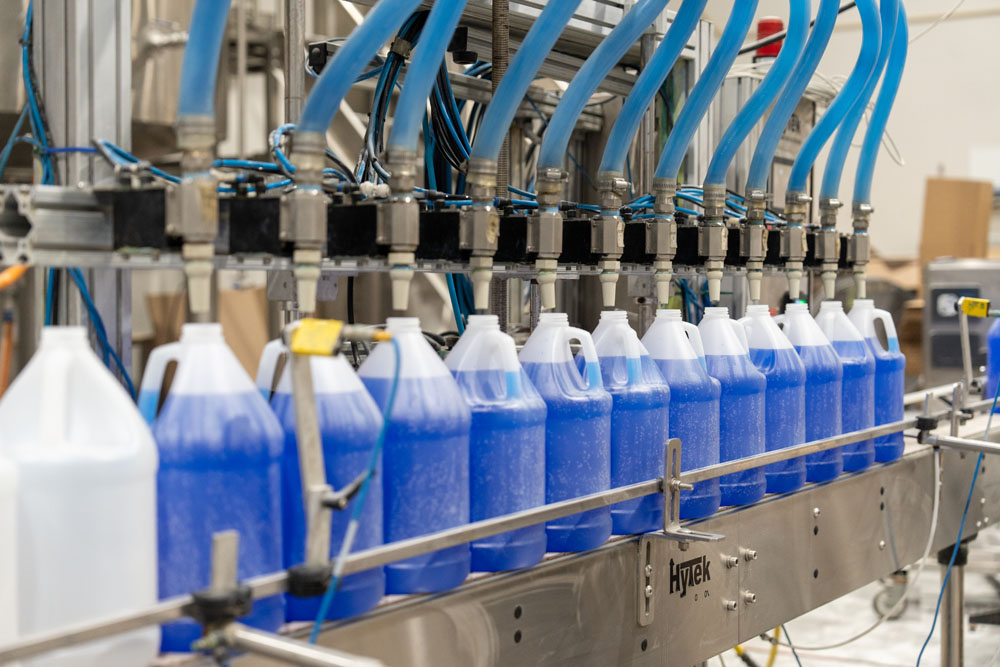

Benefits of Surfactants in Different Industries & Applications
What are the benefits of Surfactants, or Surface-Active Agents, in various industries and applications?
Surfactants offer numerous benefits across various industries and applications:
Surfactants for Personal Care and Cosmetics:
- Benefit: Enhance product performance.
- How: Improve the spreadability and emulsification of ingredients in products like shampoos and body washes.
Surfactants for Household Cleaning Products:
- Benefit: Increase cleaning efficiency.
- How: Aid in the removal of dirt, grease, and stains by reducing surface tension and improving wetting.
Surfactants in the Textile Industry:
- Benefit: Improve processing.
- How: Aid in wetting, scouring, and dyeing processes, leading to better interaction between fibers and dyes.
Surfactants in Agriculture:
- Benefit: Enhance effectiveness of agrochemicals.
- How: Improve spreading and adherence of herbicides and pesticides on plant surfaces.
Surfactants in Pharmaceuticals:
- Benefit: Enhance drug delivery.
- How: Improve solubility of drugs, facilitating their formulation and absorption.
Surfactants in the Food Industry:
- Benefit: Stabilize formulations.
- How: Act as emulsifiers and dispersing agents, contributing to the stability and texture of food products.
Surfactants in Oil & Gas:
- Benefit: Facilitate oil recovery.
- How: Alter the surface tension between oil and water, aiding in the extraction of oil from reservoirs.
Surfactants in Paints & Coatings:
- Benefit: Improve coating properties.
- How: Stabilize pigments and disperse particles, enhancing the overall performance of paints and coatings.
Surfactants in Mining & Ore Processing:
- Benefit: Aid in mineral separation.
- How: Used in froth flotation processes to selectively separate valuable minerals from ores.
Surfactants in Biotechnology & Pharmaceuticals:
- Benefit: Facilitate various processes.
- How: Used in cell lysis, protein solubilization, and other applications in biotechnology and pharmaceutical research.
Surfactants in Environmental Remediation:
- Benefit: Enhance contaminant removal.
- How: Improve the effectiveness of soil and groundwater cleanup efforts by increasing the solubility and mobility of contaminants.
Different Grades of Surfactants, aka Surface-Active Agents
There are different grades of surfactants available, depending on the application and the desired properties. For example, some surfactants are designed to be mild and gentle for use in personal care products, while others are more robust and efficient for industrial applications.
Advantages of Surfactants
Surfactants offer several advantages over other products. They can improve the solubility of substances in water, reduce surface tension, and increase the wetting ability of liquids. They also have emulsifying and dispersing properties, which help to stabilize formulations and prevent the separation of components.
Surfactants Services
Modern Chemical offers a range of surfactants services, including surfactants distribution and supply. They provide low-cost surfactants from various sources worldwide, leveraging their buying power and chemical network to offer competitive pricing. Modern Chemical also offers custom blending, warehousing, packaging, and logistics services to meet the unique needs of their customers.

Common FAQs on Surfactants
How are Surfactants Manufactured?
Surfactants are manufactured through a process that involves raw material preparation, saponification or synthesis, neutralization (for anionic surfactants), addition of additives, purification, formulation, quality control, and packaging. The specific steps vary based on the type of surfactant being produced. Raw materials, such as hydrocarbons or fatty acids, undergo chemical reactions, purification, and formulation to create the final product. This is then subjected to quality control measures before packaging and distribution. Considerations for sustainability and environmental impact are increasingly integrated into the manufacturing process.
What is the Most Popular Surfactant?
Sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) is widely used as a surfactant, especially in personal care products like shampoos and toothpaste. Known for its effective foaming and cleaning properties, SLS is a popular choice, though the most-used surfactant can vary depending on specific applications and industry trends.
What is an Example of Surface-Active Agents?
An example of a surface-active agent is sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS). SLS is widely used in various products, such as shampoos, toothpaste, and soaps, due to its ability to lower the surface tension between different substances and facilitate mixing water with oils and dirt.
What are Surface-Active Agents in Sterilization?
Surface-active agents, or surfactants, are employed in sterilization processes to enhance cleaning effectiveness before disinfection or sterilization. Detergents, quaternary ammonium compounds, alcohol-based disinfectants, and enzymatic cleaners are surfactants used to remove contaminants and organic matter from surfaces. This preparatory step ensures more efficient sterilization by preventing microorganisms from being shielded by debris, contributing to reliable microbial control in healthcare, laboratories, and other settings.
What is a Surface-Active Agent in Physical Chemistry?
In chemistry, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) is a commonly used surfactant. It is widely employed in laboratories, especially in techniques like SDS-PAGE for protein analysis, where its detergent properties help solubilize and denature proteins. SDS is also used as a wetting agent, emulsifier, and dispersant in various chemical processes due to its ability to reduce surface tension and stabilize colloidal systems.
Why request a quote from Modern Chemical for Surfactants?
Potential customers should request a quote from Modern Chemical for Surfactants because they are a trusted supplier that always delivers high-quality products on time and at a competitive price. With their extensive chemical network and expertise in surfactants, they can provide tailored solutions to meet the specific requirements of their customer’s applications. Modern Chemical’s commitment to quality and customer service makes them an ideal partner for any surfactant needs.
Modern Chemical is the best supplier that always delivers low-cost, in-spec, and on-time.
ready to get started?
have a Question?
Contact Us
Fill out the form below with as much information as possible and we will get back to you quickly.
Fields marked with * are required.
